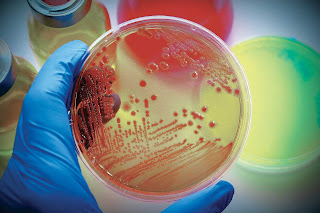
The continuous drive to increase the production, distribution and utilization of petroleum and natural gas products to meet the energy demands of the population is usually associated with some environmental pollution problems especially on the lithosphere soil and the physicochemical remediation approaches such as evaporation, dissolution, dispersion with chemical dispersants emulsifiers, and photo oxidation all found to be eco harzardous and non cost ineffective. Microbiological and Physico chemical properties of pristine soil contaminated with crude oil were assessed using standard procedures. The influence of saw dust in the remediation of the polluted soil was evaluated. Phytotoxicity of the polluted soil was assessed using maize and beans seed germination test. Most frequently occurring microbial isolates obtained were identified using molecular typing. Bacteria isolated from the pristine soil were Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Alcaligenes faecalis and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Fungi isolated were Penicillium citrinnum, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus and Rhizopus stolonifer. The most frequently occurring novel isolates were S. maltophilia, P. sordelli, B. thuringensis, F. solani, C. deightonni, P. citrinnum, and C. bertholletiae. Percentage organic carbon content of the crude oil polluted soil was 21.50 while the nitrogen content was 0.90 with a pH value of 4.69. The Percentage organic carbon of the pristine soil was 0.750 , percentage nitrogen content was 2.71 with a pH value of 5.69. This research showed that phytotoxicity test carried out on the crude oil polluted soil distorted its physico chemical parameters which has consequent toxicity on the soil, thus possibly hampering its fitness for use in crop production. Phytotoxicity test on the saw dust amended soil significantly supported plant growth with a high germination index 1G for both crops maize and beans therefore making the soil fit for use in crop production.
by Anagboso, M. O. | Orji, M. U. | Ikele, M. O. "Phytotoxicity and Microbial Activities of Crude-Oil Polluted Pristine Soil during Bioremediation with Saw Dust Amendment from Awka, Nigeria"
Published in International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (ijtsrd), ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-5 | Issue-6 , October 2021,







No comments:
Post a Comment